Configuring Android Devices for Network Analysis on MacOS
In this blog, I’m excited to guide you through the process of setting up your Android device for analyzing network traffic and intercepting it. Whether you’re simply curious about how your apps communicate or you’re gearing up for some serious pentesting, I’ve got you covered. We’ll be using tools like Burp Suite, Android Debug Bridge (ADB), and Android Studio to make this happen. Plus, I’ll walk you through the steps for both setting up on an emulator and a physical device, so no matter how you’re testing, you’re all set. Let’s get started!
Setup on an emulator
- Install android studio
The latest version is Android Studio Iguana - 2023.2.1 Patch 1 and we can install it from https://developer.android.com/studio
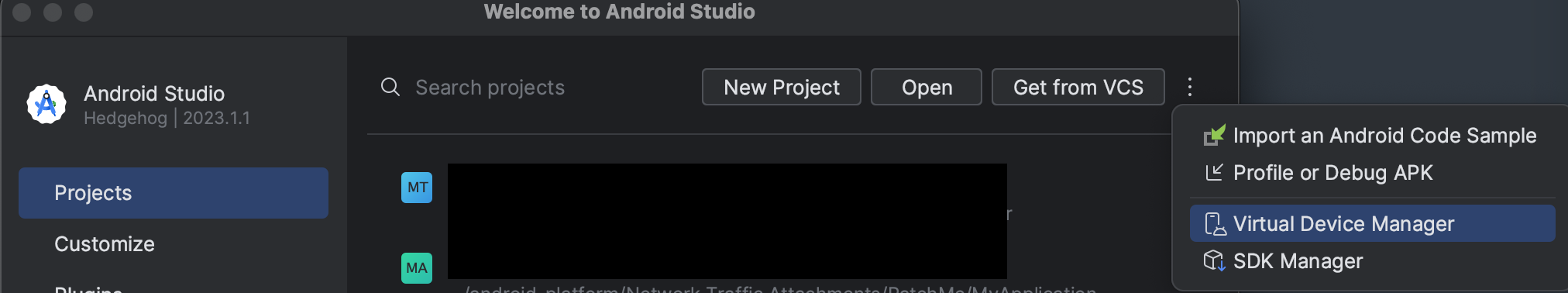
- Once installed, click on options -> virtual device manager
- Using the
+on top right, create a new virtual device.
Select Pixel 4 from the list of hardware profiles. It’s not mandatory to select that specific device but recommended. Feel free to pick the one you prefer if you think the resolution is wider than your screen size and may not fit the window.
M1-Based MacBook
From the system image window, move to the Other Images Download the Pie system image – arm64-v8a Android 9.0 (Google APIs) –
Intel-Based MacBook
From the system image window, move to the x86 tab Download the Pie system image – x86_64 Android 9.0 (Google APIs) –
Installing adb
- Install homebrew on macOS and run the command -
brew install android-platform-tools
- Start using adb
adb devices
You can also take a look at the official documentation for commands and usage -
https://developer.android.com/tools/adb
Configuring burpsuite
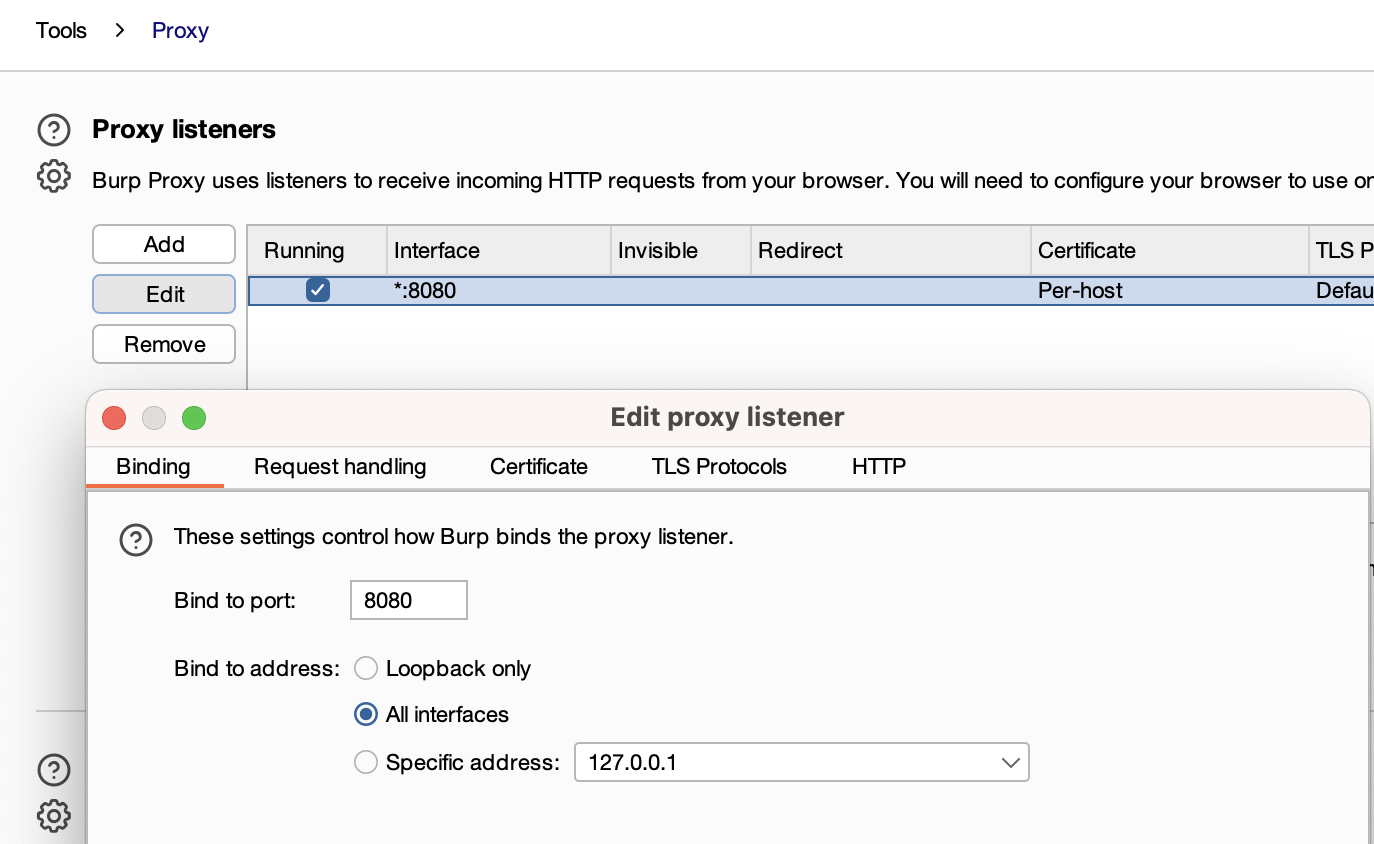
- Open Burpsuite and From Proxy > Options, edit the Proxy Listener and bind it on all interfaces:
The next steps are different for emulator and physical device
For Emulator
Open command line and get the IP address of the system using ifconfig.
Run the command below replacing BURP_ADDRESS and BURP_PORT according to your local network settings:
1
adb shell settings put global http_proxy BURP_ADDRESS:BURP_PORT
In your browser, visit http://burp/ and click CA Certificate on the top right and download the der file.
Push this file to the emulator using the command below :
adb push ~/path_tofile/cacert.cer /sdcard/Download
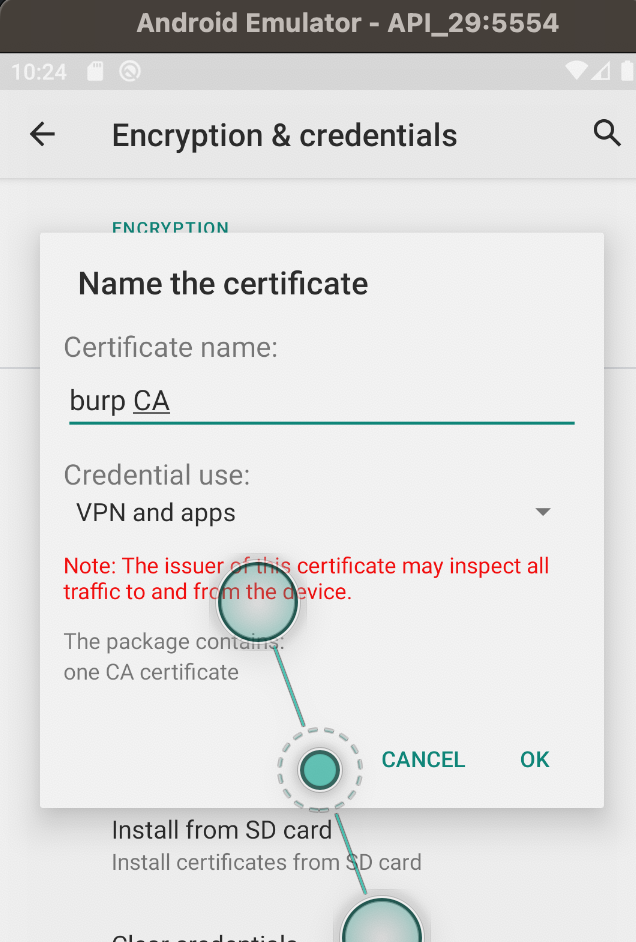
Start the emulator and on the device, open Settings > Security & location > Advanced > Encryption & Credentials
Tap Install from SD Card and select the der file. If the file is grayed out, run the following command to rename it:
adb shell "mv /sdcard/Download/cacert.der /sdcard/Download/cacert.cer"
Enter a name for the certificate and click OK
- Open the browser and visit https://example.com and if everything is correctly configured, you should not see any certificate error, and Burp is intercepting and proxying traffic.
For physical device
Start the device and go to Settings > Network & internet or click on the Wi-Fi network your device is currently connected to.
Scroll down and you will find advanced options, select Proxy > Manual.
Set Proxy hostname to the IP of the computer running Burp Suite Professional.
Set Proxy port to the port value that you configured for the Burp Proxy listener.
To connect your Android device to your computer using ADB,
- First we have to enable USB Debugging on the device
Go to Settings, scroll down and select “About phone” or “About device.” Find the “Build number” and tap on it multiple times until you see a message saying you are now a developer. Go back to the main Settings screen and now you should see a new option called “Developer options.” Open Developer options and enable “USB debugging.”
- Connecting the device to the system.
Use a USB cable to connect your Android device to your computer. Tap “Allow” to grant permission for your computer to connect to your device.
- Confirming the adb connection
Type the following command to verify that your device is connected:
adb devices
You should see your device listed under the “List of devices attached” section.
Once your device is connected via ADB, you can use various ADB commands to interact with it, such as installing apps, debugging, accessing the device shell, etc.
- To push files, the same command can be used :
adb -s <device_serial> push <local_file_path> <remote_file_path>
You can get the serial number from the output of adb devices
Hope you found this article useful!